Myth: AI is about creating superintelligent machines.
Fact: Though Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is one of the goals of AI research, we are still in the age of narrow AI. Narrow AI is a general category of AI that can handle only a single or small set of related learning tasks for a specific function.
Myth: AI focuses only on building smart robots.
Fact: Though robots are a part of AI, they do not make up all of AI. Also, not all robots are AI-enabled. Industrial robots are programmed to perform repetitive tasks. All they know is to perform the tasks they are programmed to do.
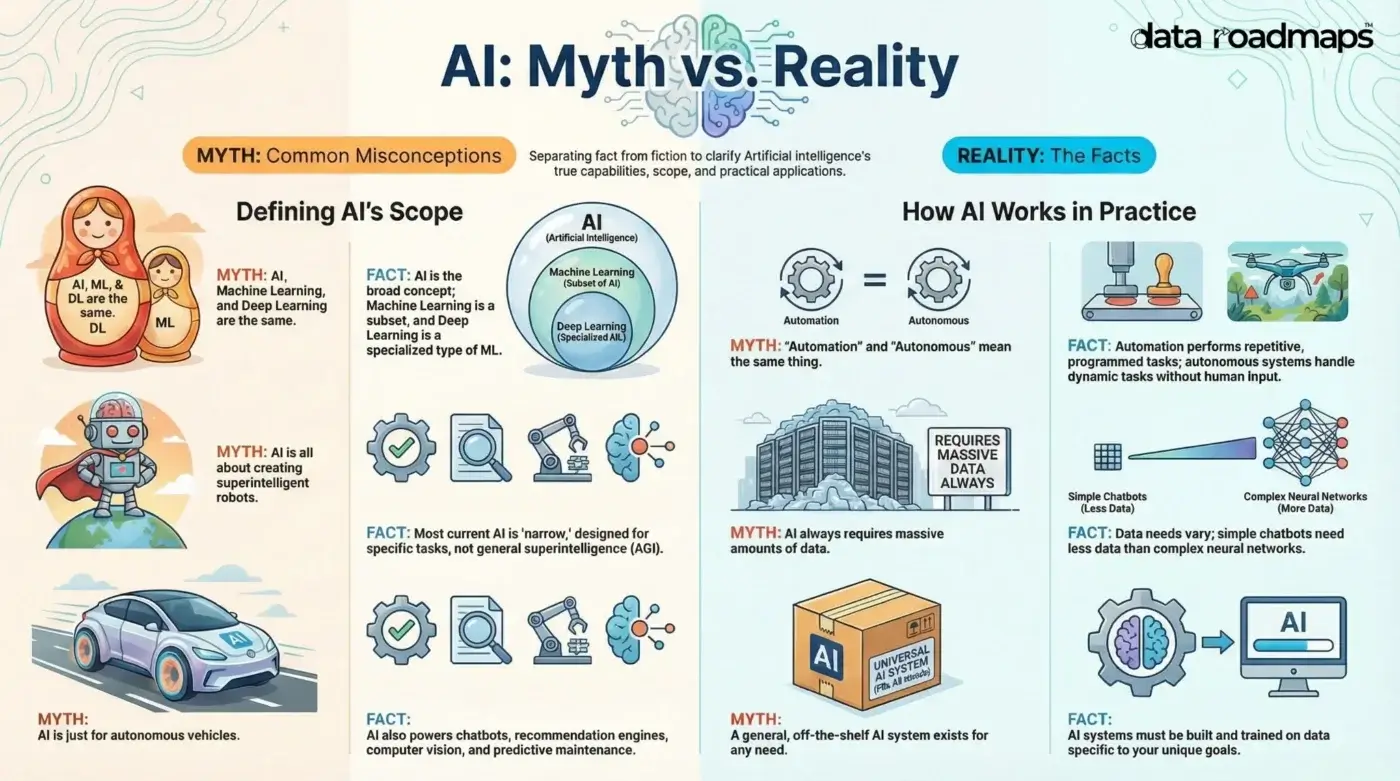
Myth: AI is about building autonomous vehicles.
Fact: Autonomous vehicles do use AI, but AI doesn’t revolve only around building autonomous systems. AI has several other applications including computer vision, AI-enabled chatbots, recommendation systems, and predictive maintenance.
Myth: Analytics and Statistics can replace AI.
Fact: In some applications, we need only analytics and statistics but not AI. In these cases, including AI may not add value to the project but only increases the time and effort involved in executing the project. However, there are applications such as facial recognition that really need AI to function. It’s important to use AI only as needed and for the right application.
Myth: AI involves complex math.
Fact: While math is at the core of the current forms of machine learning, intelligence programmed in AI involves a lot more than just complex math.
Myth: Automation and autonomous mean the same thing.
Fact: Automation is when you program a machine to perform repetitive tasks, such as industrial robots in an assembly line. Autonomous is when a machine or software can perform dynamic or complex tasks with minimal to no human involvement.
Myth: AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning are synonymous.
Fact: They are all related terms but not the same.
- AI is an umbrella term for machine behavior and functions that exhibit the intelligence and behavior of humans.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that provides machines with the ability to learn from data and improve over time through many approaches, including training (or supervised learning), discovery (or unsupervised learning) and trial and error (or reinforcement learning).
- Deep Learning is a ML approach that uses multilayered neural networks capable of handling complex needs with vast amounts of data.
Myth: AI always needs large amounts of data.
Fact: AI doesn’t always need large amounts of data. Applications such as chatbots or recommendation systems that use simple algorithms do not need a lot of data. However, applications such as complex pattern recognition or building complicated foundation models built on neural networks require a large amount of data.
Myth: A general AI system is available that can handle any AI need.
Fact: General purpose AI systems don’t exist. You cannot buy off-the-shelf general AI system. You need to build your AI systems using data specific to your needs and goals with the results that you are looking for. AI systems are primarily driven by data even though the functionalities are important. It’s important to feed the right data for AI applications to produce the right output.